

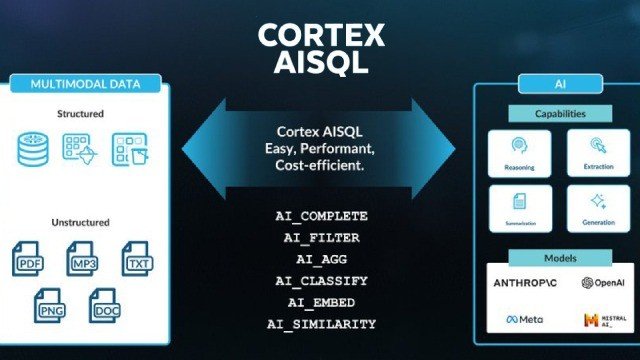
In the era of artificial intelligence, enterprises are seeking ways to extract insights from diverse data sources, including structured and unstructured data like text, image. Snowflake Cortex AISQL, a groundbreaking feature that integrates AI capabilities directly into its SQL engine. Cortex AISQL transforms traditional SQL into an AI query language, enabling analysts to process multimodal data with familiar SQL commands. This blog explores what Cortex AISQL is, its key features, benefits, empowering data professionals to unlock new analytical possibilities
Snowflake Cortex AISQL, is an innovative extension of Snowflake’s SQL engine that embeds generative AI capabilities. It allows users to analyze both structured and unstructured data—such as text, images, using standard SQL syntax. By leveraging large language models (LLMs) eliminates the need for complex data pipelines or specialized AI tools, making advanced analytics accessible to business analysts and data engineers alike.
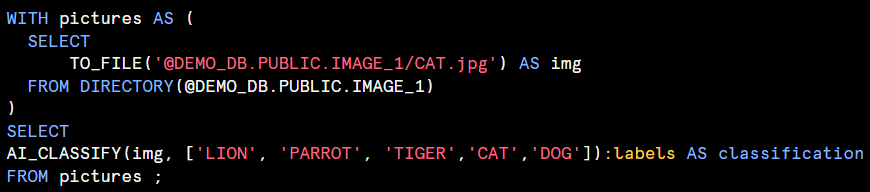
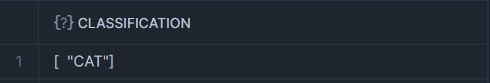
AI_CLASSIFY : Classifies text or image into user-defined categories, such as sentiment analysis(positive, neutral, negative) or image labeling.
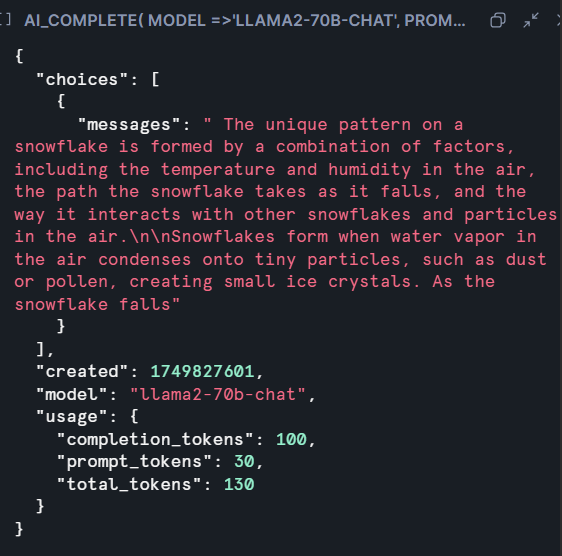
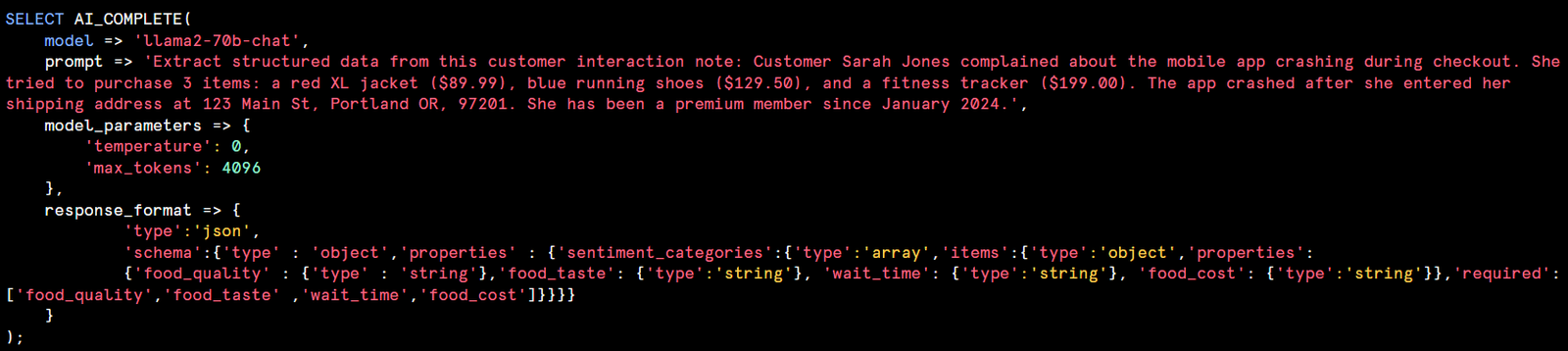
AI_COMPLETE : Generates text completions or descriptions for text and image inputs, enhancing data enrichment tasks.
AI_FILTER :Filters data based on natural language questions, applicable in SELECT, WHERE, and JOIN clauses. For example, it can identify images containing specific object or text matching certain criteria.
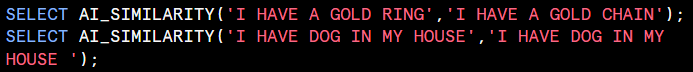
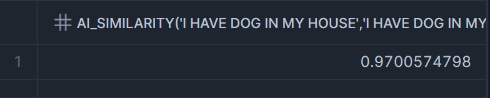
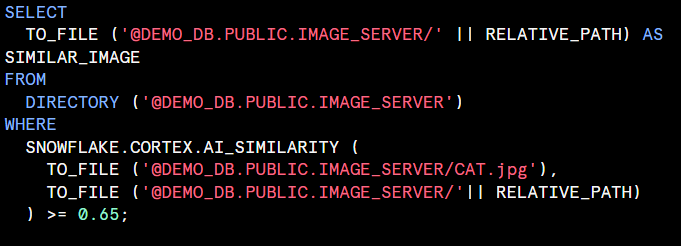
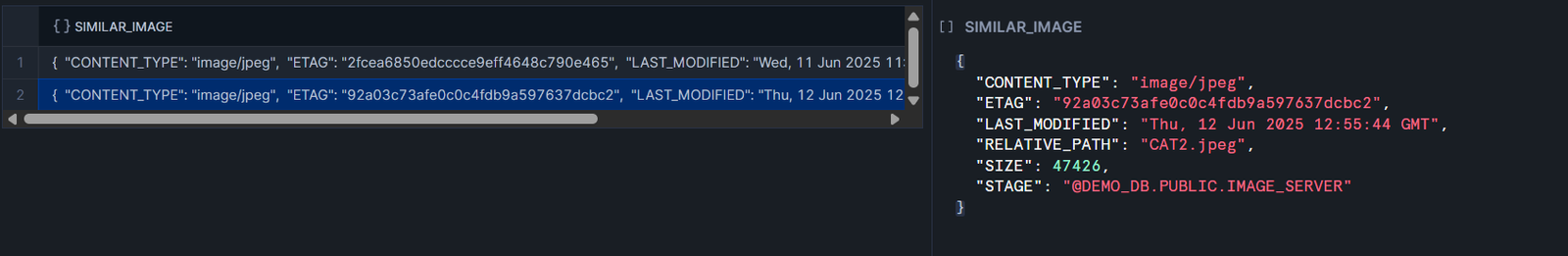
AI_SIMILARITY : Computes a similarity score based on the vector cosine similarity value of the inputes embedding vectors. Currently supports both text and image similarity computation.
AI_AGG : Reduces a column of text data using a natural language task description.
AI_SUMMARIZE_AGG : Summarizes a column of text data. Unlike AI_COMPLETE and SUMMARIZE(SNOWFLAKE.CORTEX), this function supports datasets larger than the maximum language model context window.
Snowflake AISQL divides into three types of functions, Scalar Functions, Aggregate Functions and Helper Functions. In this blog, we are going to cover Scalar Functions and Aggregate Functions only.
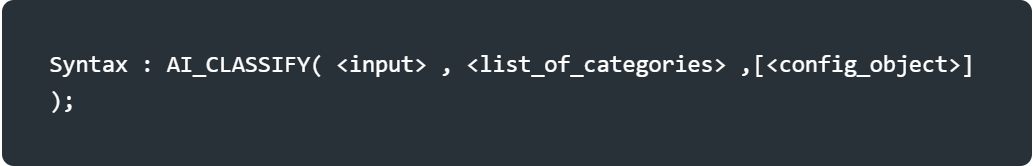
<input>: The string, image or prompt object that you’re classifying.For text classification, the input string is cae sensitive.Results may vary based on catilization.
<list_of_categories>: An array of categories with at least one and at most 500 dunique values. Categories are case sensitive. For each category, label is required(The name of the category) and description is Optional(Describe the label less than 25 words).
<config_object>: (optional) Configuration settings specified as lkey/values pairs.supported keys:
task_description : A explanation of the classification, which can help model understand the contex of the classification task and improve accuracy.
Output_mode : Set to ‘multi’ for multi-label classification.
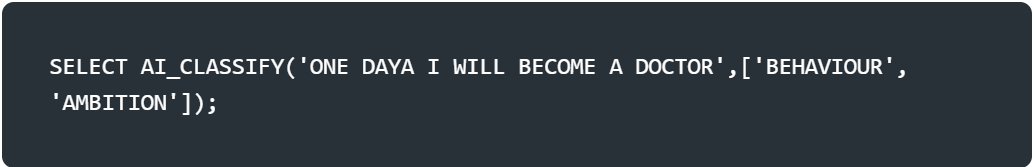
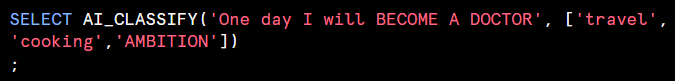
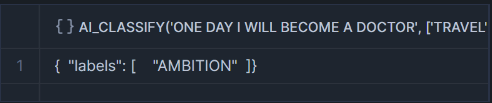
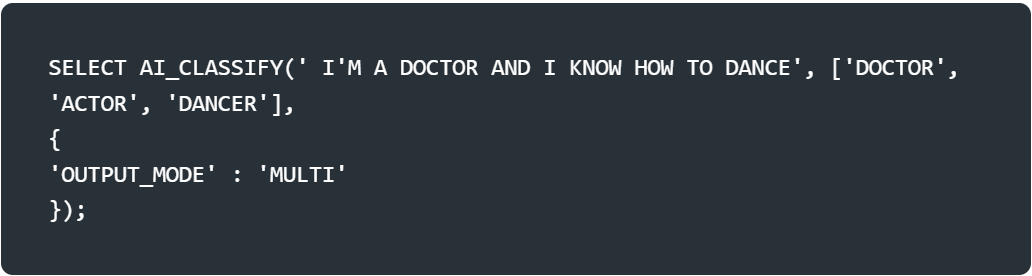
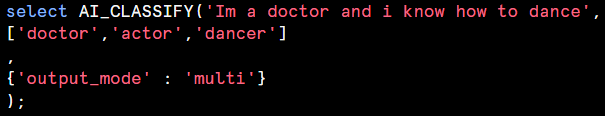
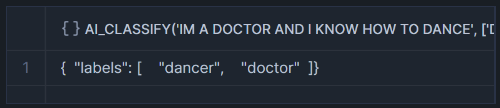

The syntax for the function depends on the type of the input that you provide. Divides into three based on arguments Single string arguments, Single image arguments, and Prompt object arguments.
Single argument: The function contains two required arguments and four optional arguments. The function can be used with either positonal or named argument syntax.
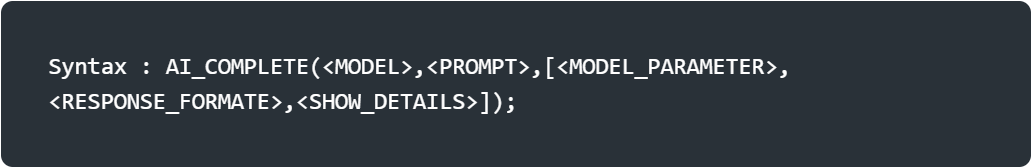
<MODEL>: A string specifing the model to be used. Specify one of the following models from Snowflake Documentation.
<PROMPT>:A string promp.
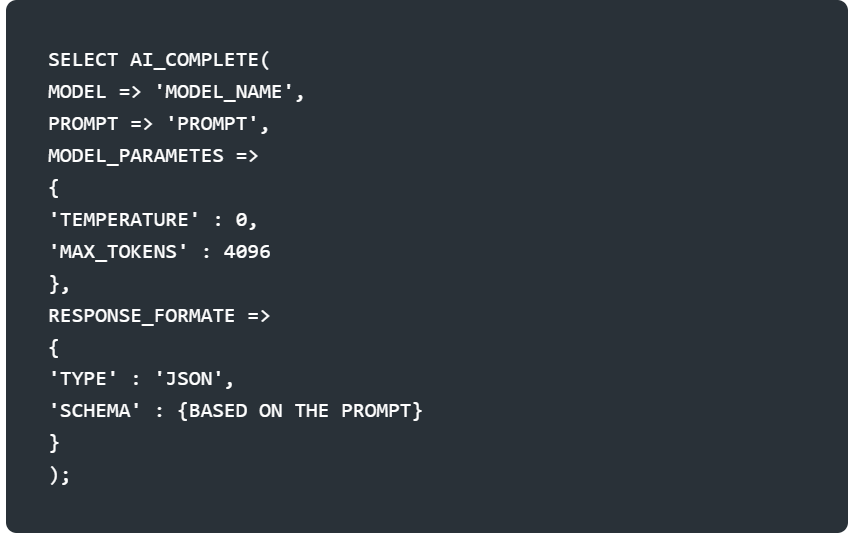
<MODEL_PARAMETERS>:An object containing zero or more of the following options that affect the model’s hyperparameters.
Temperature:A value from 0 to 1 that controls the randomness of the output of the language model. A higher value results in more diverse and random output, while low values makes the output more deterministic and focused.
Top_p:A value from 0 to 1 that controls the randomness and diversity of the language model, generally used as an alternative to temprature.The difference is that top_p restricts the set of possible tokens that the model outputs, while tempature influences which tokens are chosen at each step.
Max_token: Sets the maximum number of output tokens in the response. Small values can result in truncated responses.


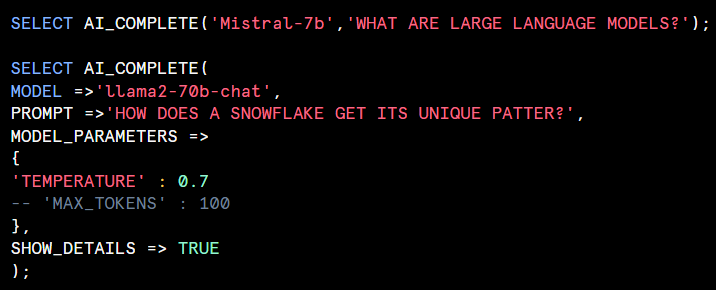
Single image: The function contains two required arguments and four optional arguments. The function can be used with either positional or named argument syntax.

<model>: Models specified on snowflake documentation.
<predicate>: A string prompt.
<file>:A FILE type object representing an image.
<model_parameters>:An object containing zero or more of the following options that affect the model’s hyperparameters.
Temperature: A value from 0 to 1 that controls the randomness of the output of the language model. A higher value results in more diverse and random output, while low values makes the output more deterministic and focused.
Top_p: A value from 0 to 1 that controls the randomness and diversity of the language model, generally used as an alternative to temprature.The difference is that top_p restricts the set of possible tokens that the model outputs, while tempature influences which tokens are chosen at each step.
Max_token: Sets the maximum number of output tokens in the response. Small values can result in truncated responses.

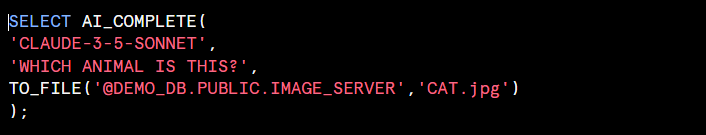

example from snowflake documentation
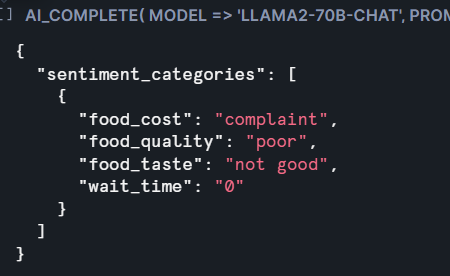
Prompt object: The function can be used with either positional or named argument syntax.
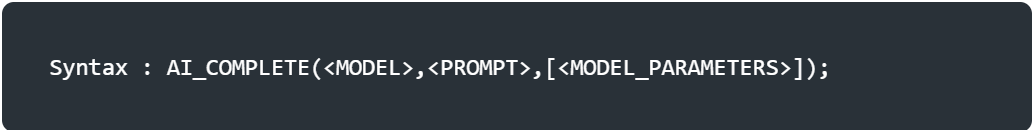
<MODEL>: A string specifying the model to be used.see on snowflake documentation .
<model_parameters>: An object containing zero or more of the following options that affect the model’s hyperparameters.
Temperature: A value from 0 to 1 that controls the randomness of the output of the language model. A higher value results in more diverse and random output, while low values makes the output more deterministic and focused.
Top_p: A value from 0 to 1 that controls the randomness and diversity of the language model, generally used as an alternative to temprature.The difference is that top_p restricts the set of possible tokens that the model outputs, while tempature influences which tokens are chosen at each step.
Max_token: Sets the maximum number of output tokens in the response. Small values can result in truncated responses.
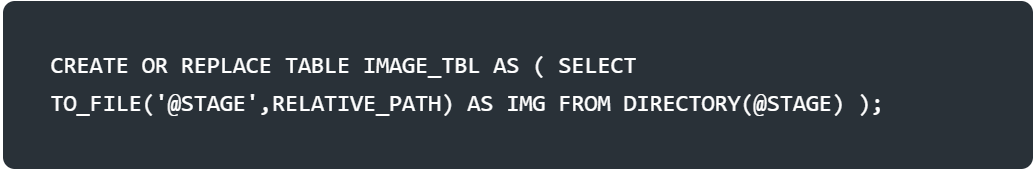
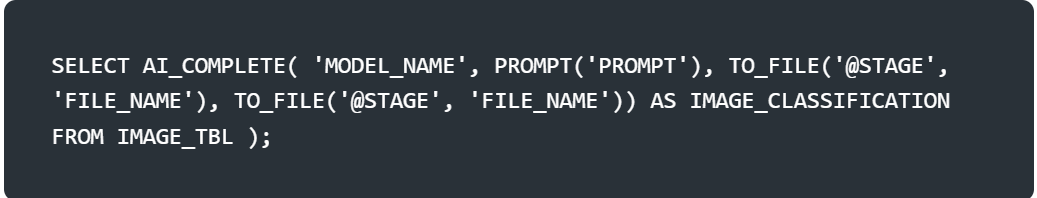
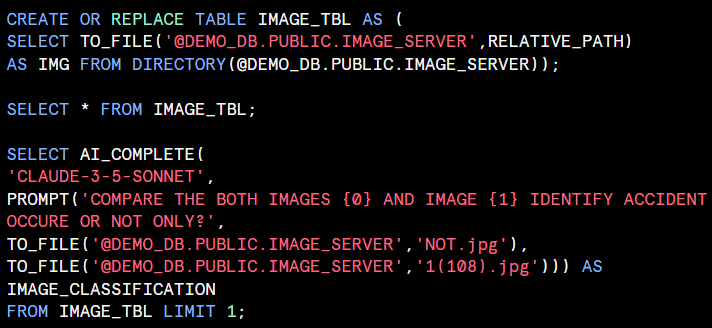
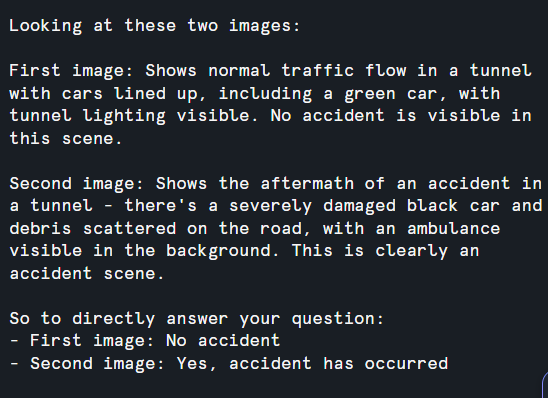
Classifies free-form prompt inputs into a boolean.



<INPUT>: A string containing the text to be classified.
<PREDICATE>: A string containing the instructions to classify the file input as either TRUE OR flase.
<file>: The column that the file is classified by based on the instructions specified in pedicate. You can use IMAGE FILE as an input to the AI_FILTER function.


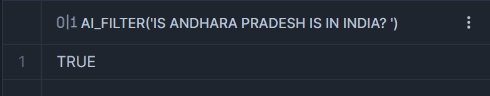

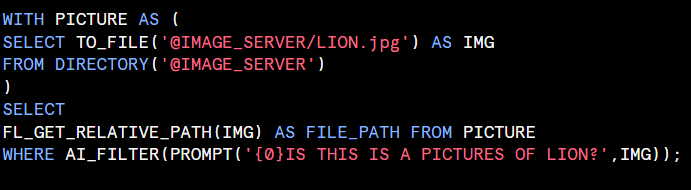
Computers a similarity score based on the verctor cosine similarity value of the inputs’ embedding vectors. Currently supports both text and image similarity computation.

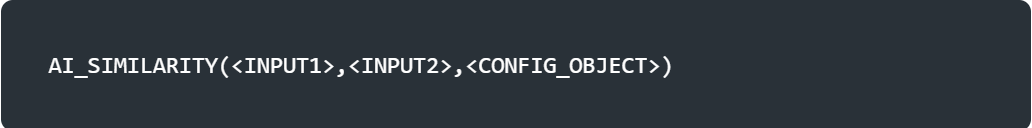
<input1>,<input2> : The strings with the text that ypu’re comparing and usig to compare the similrity score.


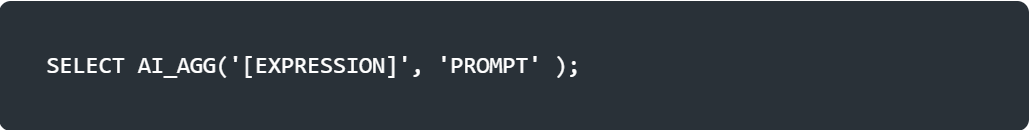
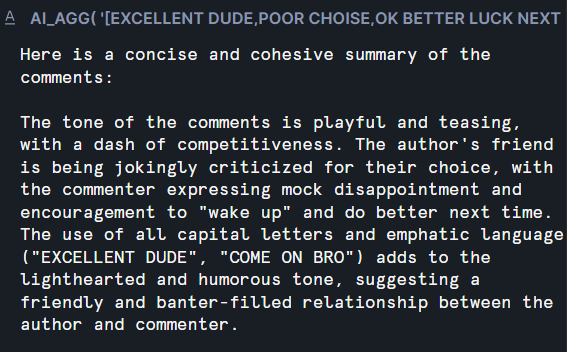
AI_AGG : Reduces a column of text data using a natural language task description.

<EXPR> : This is an expression that contains text on which an aggregation operation is tol be performed, such as restarunt reviews or phone transcripts.
<task_description> : A string containing a natural alnguage description of the aggregation to perform.

Summarizes a column of text data.
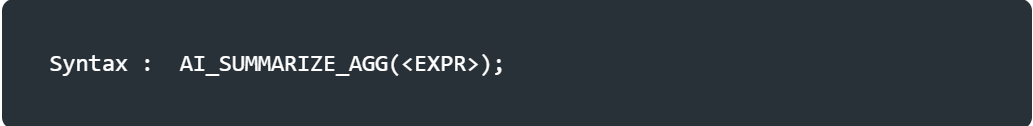
<expr> : This is an expression that contain text for summarization, such as restaurant reviews or phone transcripts.


Snowflake Cortex AISQL marks a pivotal shift in data analytics, seamlessly blending the familiarity of SQL with the power of AI to unlock insights from text, and images. By enabling analysts to query multimodal data without complex pipelines, it empowers organizations to drive innovation, streamline operations, and make data-driven decisions faster than ever. Whether you’re uncovering customer sentiments, analyzing visual assets, or bridging structured and unstructured data, Cortex AISQL offers a scalable, secure, and efficient solution. As this technology matures beyond its preview phase, it’s poised to redefine how enterprises leverage AI in the data cloud.